General Dermatology
COMMON SKIN DISORDERS
The skin is the largest organ of the body, and as such also has a large number of disorders and diseases associated with it. There are more defined and distinct diseases involving the skin than there are for any other organ in the body. At present there are over 1200.
We at the Derma Treat Center treat them all. Here are 15 of the most common skin disorders:
A short guide to some of the most common skin conditions
Acne Vulgaris
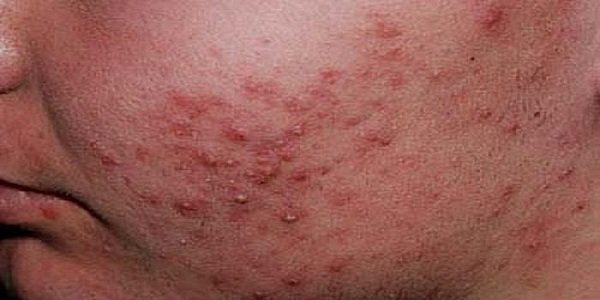
Acne is an inflammatory disease of the pilosebaceous units in the skin of the face, neck, chest and upper back. Typically, it first appears during early puberty when androgenic stimulation triggers excessive production of sebum and abnormal follicular keratinization, colonization by a Gram-positive bacterium (Propionibacterium acnes) and local inflammation. P. acnes produces inflammation through the production of extracellular products such as lipases, proteases, hyaluronidases and chemotactic factors.
Clinically acne is Characterized by the presence of Greasy skin (seborrhoea), Non-inflamed lesions ie comedones including blackheads and whiteheads . Inflamed lesions include papules, pustules and nodules. Scarring is a common consequence of scratching and rubbing of the inflamed lesions and Pigmentation a problem especially common in dark skin.
Treatment for acne depends on the patient's age and sex, the extent and the severity of the acne, how long it has been present, and response to previous treatments. Treatment for mild acne includes topical anti-acne preparations, lasers and lights. Treatment for moderate acne adds acne antibiotics such as doxycycline, azithromycin etc. and/or antiandrogens such as birth control pill. Treatment for severe acne may require a course of oral isotretinoin.
Atopic Eczema
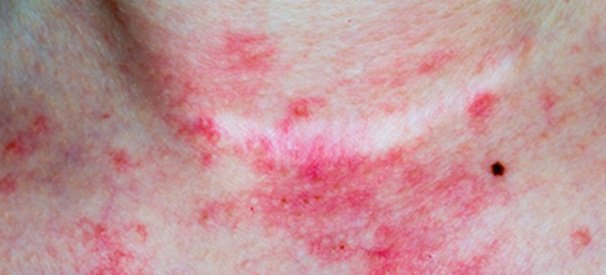
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is the most common form of eczema and makes your skin itchy, red, dry and cracked.
It's a long-term condition in most people, although it can improve over time, especially in children, who often grow out of it.
It can affect any part of the body, but most commonly affects:
Treatment, which includes using moisturisers and topical steroids, can help relieve symptoms.
Find out more about atopic eczema, including treatment advice.
Cold Sores
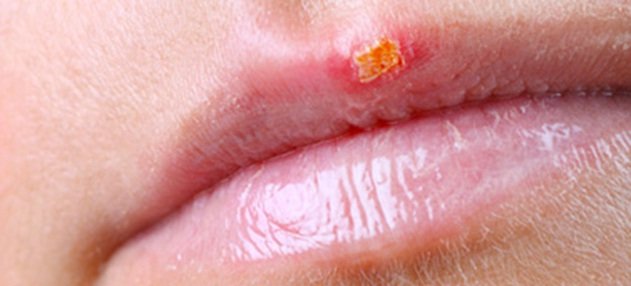
Cold sores are small blisters that develop on the lips or around the mouth, caused by the herpes simplex virus.
They often start with a tingling, itching or burning sensation around your mouth. Small fluid-filled sores then appear, usually on the edges of your lower lip.
Cold sores usually clear up without treatment within 7 to 10 days, but antiviral creams are available from pharmacies over the counter. These can help ease your symptoms and speed up the healing time.
Find out more about cold sores and how to treat them.
Hives (urticaria)
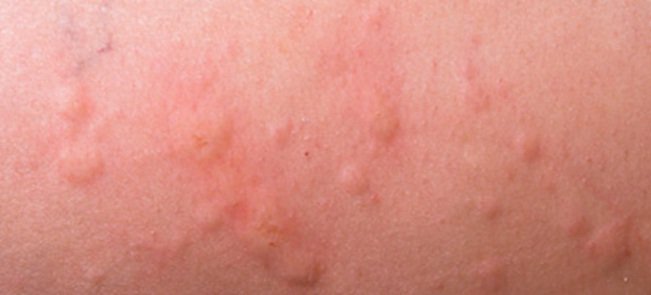
Urticaria – also known as hives, weals, welts or nettle rash – is a raised, itchy rash. It may appear on one part of the body or be spread across large areas.
In many cases, you don't need any treatment because the rash gets better within a few days.
If the itchiness is uncomfortable, antihistamines can help and are available over the counter at pharmacies.
See your GP if your symptoms don't go away within 48 hours.
Find out more about hives, including treatment advice.
Impetigo
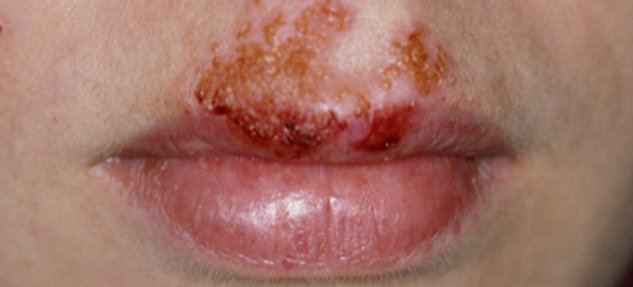
Impetigo is a very contagious skin infection that causes sores and blisters. There are two types:
It's more common in children, but can affect anyone.
The infection is likely to clear up by itself within three weeks, but it's a good idea to see your GP for a diagnosis as the symptoms are similar to other, more serious conditions.
Your GP can also prescribe antibiotic cream or tablets to get rid of it quickly.
Find out more about impetigo, and how to treat and manage the infection.
Itching
Itching can affect any area of the body. Mild, short-lived itching is common, but it can sometimes be severe and frustrating to live with.
There are things you can do that may help, including:
Antihistamine and steroid cream may help relieve itching caused by certain skin conditions.
Find out more aboutv itching, including treatment advice.
Psoriasis
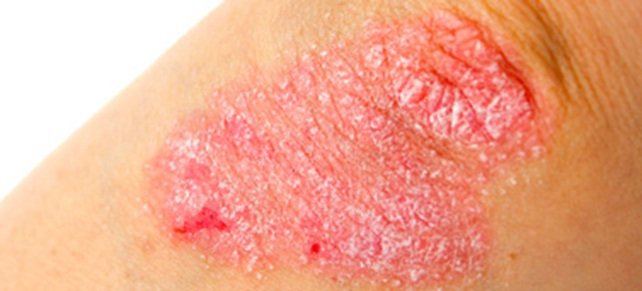
Psoriasis typically causes flaky red patches of skin covered in silver scales. The patches usually appear on the elbows, knees and the lower back, and can be itchy or sore.
For some people, psoriasis is just a minor irritation, but for others it can have a major impact on their quality of life.
People with psoriasis usually have periods when they have no or mild symptoms, followed by periods when symptoms are more severe.
Most people are treated by their GP, but you may be referred to a skin specialist called a dermatologist if your psoriasis is severe.
Although there is no cure for psoriasis, treatments can improve your symptoms. They include:
Find out more about psoriasis and how to treat it.
Ringworm
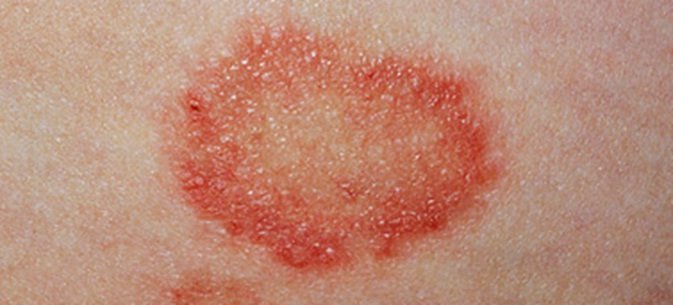
Ringworm is not a worm, but a contagious fungal infection that typically appears on the arms and legs, although it can appear almost anywhere on the body. It causes a red or silvery scaly rash in the shape of a ring.
Anyone can get ringworm, but it's more common in children.
You can treat ringworm with antifungal creams, powders or tablets, which are available over the counter from a pharmacy.
You may need to see your GP if you aren't sure it's ringworm, or if the infection doesn't clear up after using a pharmacy treatment for two weeks.
Find out more about ringworm and other fungal infections, including treatment advice.
Scabies
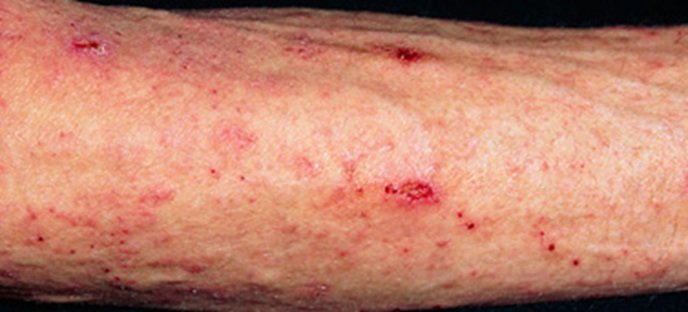
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin. The main symptoms are intense itching that gets worse at night, and a rash of tiny red spots.
See your GP if you think you have scabies. It's not usually serious, but treatment – normally a cream or lotion – is needed to kill the scabies mites.
Find out more about scabies and how to treat it.
Vitiligo
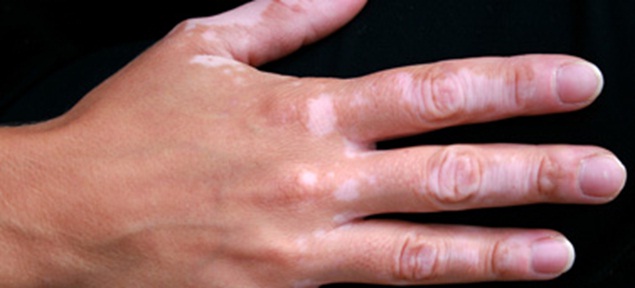
Vitiligo causes pale white patches on the skin that vary in size and can occur anywhere.
They are more noticeable on areas that are exposed to sunlight, such as the face and hands, and on dark or tanned skin. Vitiligo on the scalp can make your hair go white.
Vitiligo is a long-term condition. It's not contagious. You should see your GP to if you suspect vitiligo.
Treatment aims to improve your skin's appearance, and includes:
Find out more about vitiligo, including treatment advice.
Warts and verrucas
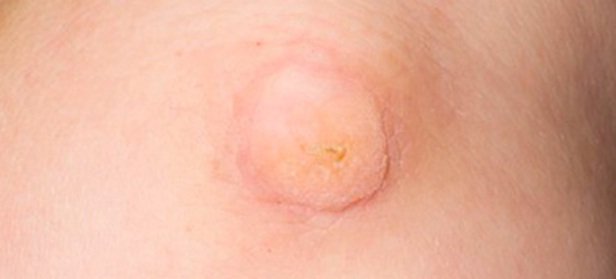
Warts are small lumps that can appear anywhere, but usually affect the hands and feet. A wart on the foot is called a verruca.
Most warts are harmless and clear up without treatment, but you might decide to treat your wart if it's painful, or if it's causing discomfort or embarrassment.
Treatments include: